"Value is created through the collaboration of business, data, and IT functions."
Head of Data and Analytics, Kemira Oyj
Picture: Kemira
A Data Platform that utilizes IoT data from a production facility lays the foundation for the creation of value through data and analytics.
Kemira is a leading global company that manufactures sustainable chemical solutions for industries that use a significant amount of water. The company's competitive edge is based on products and expertise that best support the process and resource efficiency and quality of its customers. Kemira's clients are in the pulp and paper industry, water treatment, as well as the oil and gas industry. In 2020, Kemira's turnover was approximately 2.4 billion euros, and it employed around 5,000 people.
Kemira's vision is to be a data-driven organization. It is generally believed that by smartly utilizing data, companies can enhance their operations, develop, and innovate new business. At Kemira, too, data and analytics are intended to create business value and support data-based decision-making, says Head of Data and Analytics.
To extract value from data, it requires cross-organizational understanding of the available data, a functioning data architecture, and defined data management models. On top of these, practices, expertise, and processes can be built that support the use of data and decision-making. Kemira's data and analytics strategy is closely linked to the company's business strategy to maintain a clear focus.
Kemira's Head of Data and Analytics notes that achieving a data-driven organization requires cooperation between business, data experts, and the IT function. No single unit can succeed in this task alone.
To support the vision, it is also crucial to ensure that the organization has the right kind of expertise, the right people in the right places, and a suitable partner network to help implement projects. When these areas are in order, the organization can rapidly execute innovation projects and agilely pilot new things. This leads to the creation of business value and support for data-based decision-making.
One concrete example of a capability designed to support Kemira's vision of a data-driven organization is a unified Data Platform, Kemira Data Hub, where data is stored and processed. For example, IoT data from the Oulu plant is stored and processed, among other data.
Kemira Data Hub brings together process and automation data produced by the factory into a single platform.
Data is used to seek answers to questions such as:
At best, the answers obtained from data can yield concrete financial benefits, such as through more efficient processes or by avoiding production downtimes.
Although the data brought to the Data Platform has been locally used at the Oulu plant so far, the aim now is to collect, combine, and utilize data beyond just one production facility.
As an example, the Head of Data and Analytics mentions, for instance, the operation of a pump in a particular factory or production facility. Even if data from the device is available locally in one factory, by aggregating data from several pumps across different factories, broader lessons and observations can be learned from the data. Combined data can help, for example, in predicting the likely breakdown of equipment or in finding optimal maintenance intervals.
The implemented Data Platform capability is easily scalable. The costs of replicating the solution are minimal, and new data sources, such as new production facilities, can be added to the Data Platform conveniently.
”Combined data can help, for example, in predicting the likely breakdown of equipment or in finding optimal maintenance intervals,” she outlines.
In the future, Data Platform will enable the construction of comprehensive reporting and analytics based on data produced by the factory’s automation system. The automation system measures the hydrogen peroxide production process with various meters or tags. These meters produce data at a millisecond frequency. This meter data is brought into the Data Platform, where it can be aggregated, analyzed, visualized, and shared.
Bringing IoT data from the Oulu plant to the Data Platform means that data from the automation system is almost real-time and also stored for future needs.
Previously, data produced by the automation system was mainly used in a manually compiled form. With the Data Platform, manual processes related to data handling have now been automated. Time spent on reporting is saved from report generation to its analysis.
Data Platform enables not only the collection, modification, and merging of data but also its sharing. Data can be agilely combined with other data and shared internally, for example, with research and product development units.
For data analysis, the most suitable tools at the time, such as Machine Learning algorithms, can be used. Automation system optimization can now leverage machine learning and statistical analysis. Generally, this results in quality improvements and cost reductions. Data visualization also plays a key role. For data to communicate something to the recipient, it must be in an understandable form.
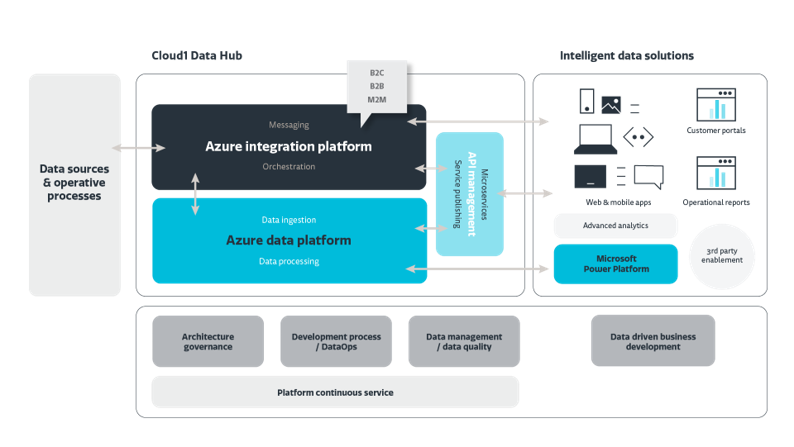
The implemented Data Platform was developed using an agile model. The development targets for 2-3 week sprints were defined and prioritized one sprint at a time. From Cloud1's side, a dedicated Kemira Data Hub team was involved in the project.
Agile development allows for flexibility in that the items to be developed in sprints don’t need to be precisely defined in advance, but prioritization and development targets can be implemented as the project progresses. Especially when the solution is new, this method brings flexibility and responsiveness to the project.
Kemira's Head of Data and Analytics emphasizes that collaboration between business, and data and IT functions is also crucial during the development phase of the solution. It's important for each development target to have a clear owner who is eager to push the matter forward.
The best outcome is always achieved through good collaboration.
Could your data strategy better support your business? Let’s discuss more: myynti@cloud1.fi.
